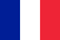
Psoriasis is an inflammatory chronic disease of the body, accompanied by predominant damage to the skin with the formation of erythematous spots and plaques with clear boundaries and silvery scales on the surface.
The course of this disease is characterized by periods of exacerbation and remission (reduction of symptomatic manifestations). Unfortunately, medicine has not yet determined the exact and reliable cause of psoriasis, but the hereditary factor that contributes to the triggering moment of the appearance of this disease, along with the triggering factors, has been clearly noted. A relationship between psoriasis and antigens of the HLA system was found.
Between 1 and 5% of the world's population suffers from this very unpleasant condition, and white people are at a higher risk of developing psoriasis than black people.
The disease can manifest itself at any age, but the periods of 20-30 and 50-60 years of age are considered critical.
It is important!Psoriasis is not contagious to others, but it causes discomfort to the patient himself, because the rash during the disease is not only a cosmetic defect, but also accompanied by unpleasant itching. In addition, the manifestation of psoriatic arthritis is possible, which significantly worsens the patient's quality of life.
Basically, rashes are localized on the scalp, on the surface of elbows and knees, skin folds and genitals. The area around the nails, hips and eyebrows can be affected often. The nature and appearance of the rash depends on the type of psoriasis.
Causes of psoriasis
The nature of the formation of psoriasis has not yet been discovered by medicine, some doctors talk about autoimmune causes. The second theory that explains the occurrence of the disease is a violation in the normal process of maturation and division of skin cells. Heredity and stress are also considered causes.
Psoriasis, genetic predisposition to allergies and frequent disruption of the skin's barrier function (strong friction, chemical exposure, effects of alcohol-containing products) can lead to exacerbation of the disease.
- Koebner's phenomenon is the appearance of new rashes at the site of skin irritation in the acute phase of some dermatoses;
- Sunburn or other types of burns;
- HIV infection;
- beta-hemolytic streptococcal infection causing guttate psoriasis;
- Use of drugs (especially beta-blockers, lithium, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors);
- Severe emotional stress;
- Alcohol consumption;
- smoking tobacco;
- Obesity;
- Hormonal imbalance in women, especially during menopause and pregnancy;
- Disorders in the digestive system.
The main reason for the development of the disease is the excessive, accelerated growth and division of skin cells, together with the inflammatory process in the dermis. That is, the skin cells located in the lower layer of the epidermis begin to grow rapidly and put pressure on the cells above. This process is accompanied by significant peeling of the skin and is called parakeratosis. Overstimulation by the immune system is believed to be the key link in this mechanism.
Symptoms and signs of psoriasis
Rashes associated with psoriasis are asymptomatic or accompanied by itching. Most often, they are localized on the scalp, extensor surfaces of the knees and elbows, sacrum and hips (especially in the gluteal fold) and genital area. Fingernails and toenails, the skin of the eyebrows, armpits and navel can be damaged. Rashes can be combined with lesions and between them can cover large anatomical areas and areas of the skin. Depending on the type of psoriasis, the rash can have different external manifestations.
As a rule, rashes are located discretely and are represented by erythematous papules or plaques covered with dense, silvery, shiny scales. The rash appears gradually. Remissions and exacerbations occur spontaneously or after exposure to provoking factors.
5-30% of patients develop
It is important!Psoriasis does not threaten the patient's life, but it disturbs the patient's self-image. In addition to the change in the patient's appearance, it takes a lot of time to treat skin rashes, maintain the cleanliness of clothes and bedding, which greatly reduces the patient's quality of life.
Types of psoriasis
vulgar (ordinary or chronic plaque) psoriasis, the rash has the appearance of individual plaques covered with a silvery crust. As the disease progresses, plaques may coalesce. Among all subtypes, this type of psoriasis is the most common and accounts for about 90%.reverse psoriasis accompanied by rashes that appear in the area of natural folds and can cause cracks.guttate psoriasis It is characterized by numerous skin rashes with a diameter of 0. 5-1. 5 cm. Often occurs after streptococcal pharyngitis.palmoplantar psoriasis manifests itself in the form of plaques that can be combined on the palms and feet.nail psoriasis it affects the nail plates in the form of dotted indentations and grooves with discoloration and thickening of the nail. Nail changes with psoriasis often resemble changes with a fungal infection.pustular psoriasis it is accompanied by the formation of pustules on the palms, feet, or perhaps damage to one of the fingers. It can also be a generalized form.erythrodermic psoriasis in patients with psoriatic plaques, the plaques themselves are soft or absent, presenting as a sudden or gradual appearance of redness. It usually appears due to improper treatment of vulgar psoriasis.
Psoriasis diagnosis methods
When symptoms of psoriasis appear, the patient should consult a dermatologist. He will conduct an external examination of the affected areas of the skin and collect a complete medical history.
Psoriasis has a common similarity with other dermatological diseases, especially in the early stages of manifestation. It is important to exclude the presence of fungal infections on the hands and nails. The seborrheic type of psoriasis requires a specific differential diagnosis to exclude seborrheic eczema, pityriasis rosea, and papular syphilis.
In the case of active disease and large lesions of areas of the epidermis, visual analysis of scraps is used. In the process of squeezing, the crust is strengthened. On the removed scale, a smooth, thin film is visible, which comes off under mechanical action and reveals a surface moistened with drops of blood.
In most cases, the diagnosis of psoriasis is not difficult, just checking the patient's skin is enough. The doctor must exclude errors in the diagnosis and determine the presence of other diseases and other pathologies occurring against the background of psoriasis.
Rarely, diagnosis requires a biopsy. If there are non-classical clinical signs, its need should be considered. Depending on the area of the affected skin, the severity of the disease is mild, moderate and severe. Damage to less than 10% of the skin corresponds to mild severity. There are more sophisticated methods to assess the severity of the disease, but these are used in clinical trials.
Treatment of psoriasis
There are many factors on which the development of the disease and its various manifestations depend. Therefore, many treatments have been developed for psoriasis. Often these methods are combined, including both drug and non-drug interventions.
The treatment plan is drawn up depending on the severity of the disease, the area of the affected skin and the severity of symptoms such as redness, itching, peeling. Age and sex, stage of the disease and general condition of the patient, presence of concomitant diseases are also taken into account, as they can limit the choice of treatment methods.
Treatment of psoriasis should lead to reduction of clinical manifestations (rash and other symptoms), improvement of the patient's general condition and restoration of his working capacity.
Since there is a risk of liver damage when treating psoriasis, it is necessary to follow a diet and take proper care of the skin. In such cases, it is recommended to reduce the amount of fatty foods in the patient's diet, to avoid alcohol, sweets (simple sugars) and starchy foods. The emphasis in the diet should be on proteins: lean meat, fish, dairy products, vegetables and fruits. Be sure to pay attention to allergic reactions or intolerance to certain products.
To improve the patient's quality of life and get rid of the disease, it is necessary to use an integrated approach:
Local treatment –Ointments and creams fight well with peeling and itching in small areas where the disease is localized. Hormonal ointments, salicylic acid, retinoids, and moisturizing creams are particularly effective in treating psoriasis on the face and hands.Drug therapy when ointments do not help, it is used as an additional method of effective treatment of psoriasis. Medicines reduce the inflammatory process, eliminate swelling and itching, inhibit the increased activity of skin cells. But it is worth considering that tablets have many side effects (increased fatigue, loss of appetite, high blood pressure). Therefore, it is very important to follow all the doctor's recommendations regarding the dosage of the drug.- Use when psoriasis is localized on the head and neck
medicated therapeutic shampoos : antifungal, tar, containing corticosteroids. Shampoo eliminates pathogens of pathological inflammation, removes scales, relieves itching and burning. Therapeutic antihistamine injections prevents severe itching, biological drugs have a beneficial effect on the immune system.
Unfortunately, there is no way to completely cure psoriasis today. Any treatment for psoriasis is aimed at eliminating the symptoms of the disease for a long time and prolonging the remission. Although the chronic course of the disease is slow, psoriasis treatment is necessary, because the long-term absence of therapy can lead to disability of the patient.